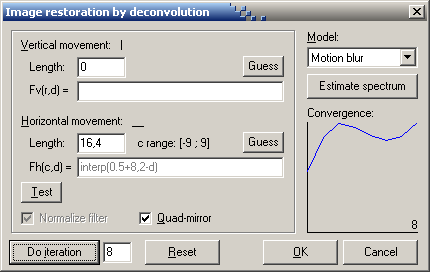
This feature allows advanced reconstruction of blurred images. Both motion blur, out-of-focus
blur and other errors are handled. In the example below the camera was moved what correspond to
about 17 pixels while the picture was taken. This distance can be estimated by looking at the details
in the background: A tree is approximately 17 pixels wide. To make the program estimate the moved distance,
click the Guess button. For this particular image the estimate made is 16.4.
Note that the bird is moving, and therefore cannot be reconstructed using the same model as the background.
For some pictures the movement estimate will be best with Quad-mirror turned on, and for some it will be best
with this option turned off. The purpose of Quad-mirror is to compensate for the periodicity assumption made
in the Fourier transform.
If the motion is neither horizontal nor vertical, the picture must be rotated before
deconvolution / deblurring. This might, however, reduce the quality of the reconstruction somewhat.
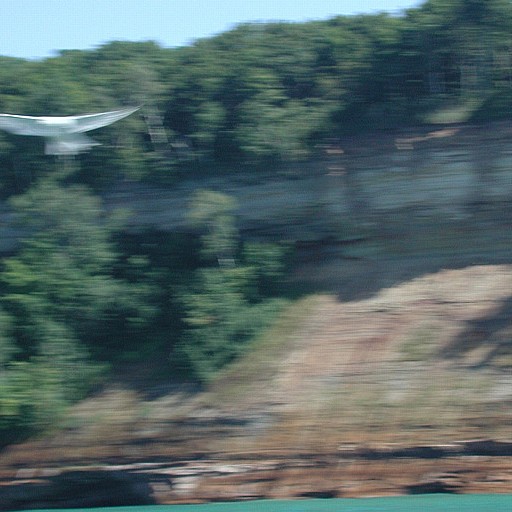

Clip from original photograph by Ching-Kuang Shene.
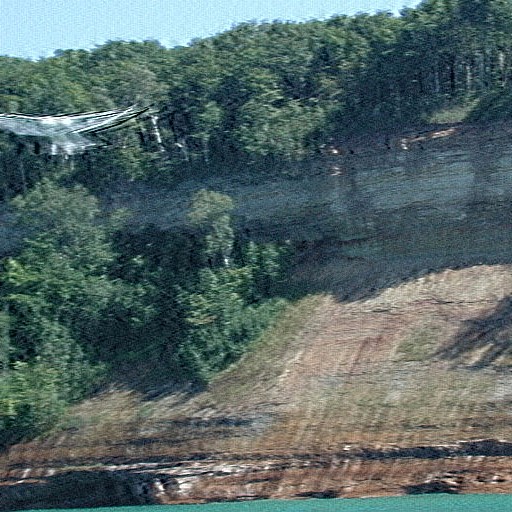

Restoration after 8 CGLS iterations.
For out-of-focus blur, the Circular blur model will probably give the best results.
The default setting will sharpen an image which is slightly unsharp. To find out which
radius gives the best result use the Test button. This will produce a number of
reconstructions with different filter radius. Enter an iteration count (~12), click Test,
enter the lower and upper bound for the radius and the number of reconstructions to generate.
If the result is too grainy then reduce the number of iterations.
 Original |
 Corrected, circular blur 12 iterations, radius=3.6 |
Adaptive noise removal (Alt-A) can remove high-frequency noise from most images.
Unlike the smoothing algorithm for noise reduction found in many image processing programs,
Adaptive noise removal works without unsharpening edges in the image.
Not only will noise reduction improve the visual impression of an image, it will also make
JPEG compression more effective producing smaller files with the same quality selection.
The example is the result of applying the filter to the deconvolution image
above using the default options.

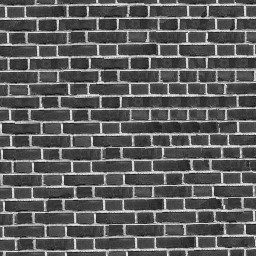
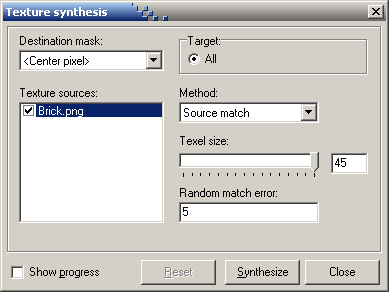
Texture synthesis (Special menu) is a tool for generating textures from a sample
or filling holes in an image.
Texture generation is performed by creating a blank image (File | New) and
opening one or more sample images and selecting them in the Texture sources box.
Destination mask tells the program what part of the image is known. In texture generation
we say that only the center pixel is known and all other pixels should be synthesized.
Method should be Source match and the Texel size the approximate size of the pattern
features. In the example below a large brick is about 45 pixels wide. If the random error is set
larger than 0, some more computation time is required but the program might be better at synthesizing
high-frequency elements.
| Sample | Sample |
 |  |
| Synthesized texture | Synthesized texture |
 |  |
| Texture sample | Fixed image |
 |  |